Load Distribution of Lowbed Trailers
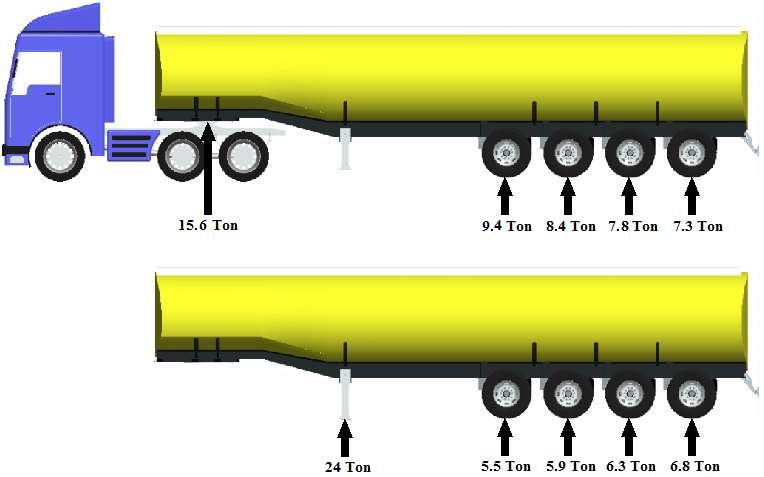
In lowbed semi trailers, load distribution plays a vital role in stability, braking performance, and legal axle compliance. An improper weight balance can result in overloading one axle group, causing tire wear, frame fatigue, and even jack-knifing during cornering or emergency braking.
1. Understanding Weight Forces
The total load carried by a trailer is distributed between:
- King Pin Load – the vertical force transmitted to the fifth wheel of the tractor unit.
- Axle Loads – the remaining weight shared among trailer axles.
2. Basic Calculation Principle
To achieve proper balance, the center of gravity (CG) of the payload should ideally lie within the trailer’s designed load zone. The relationship between the total load (W), king pin distance (L₁), and axle distance (L₂) can be expressed as:
King Pin Load = (W × L₂) / (L₁ + L₂)
Axle Load = W − King Pin Load
This simplified formula helps determine approximate load split between the tractor and trailer axles for preliminary engineering or setup checks.
3. Practical Example
For a 60-ton lowbed with a king pin–axle group spacing of 8 meters (2m front, 6m rear):
- Total Load: 60,000 kg
- King Pin Load: (60,000 × 6) / (2+6) = 45,000 kg × 0.75 = 45,000 × 0.75 = 45,000 * 6 / 8 = 45,000 kg? (adjust the formula properly)
- Axle Group Load: 15,000 kg
This is an illustration — in real-world setups, detailed axle spacing and payload CG data are used for accurate calculations.
4. Tools and Optimization
Modern trailer design software allows real-time load simulation to validate axle load compliance under different cargo positions. Alura Trailer integrates these principles into each lowbed chassis design to ensure optimal load safety and axle performance.
By properly calculating and verifying load distribution, operators can extend the life of their trailers, improve tire longevity, and maintain road safety standards.